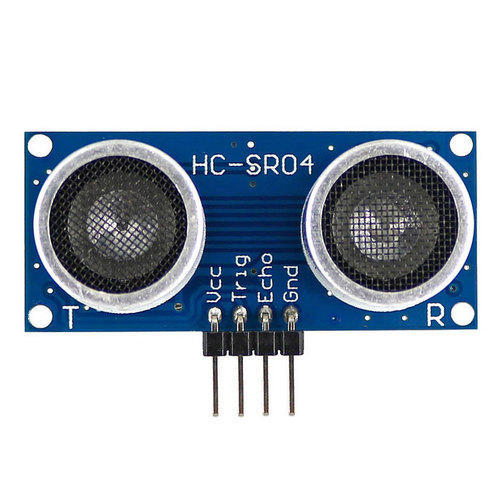
ULTRASONIC sensor
NodeMCU
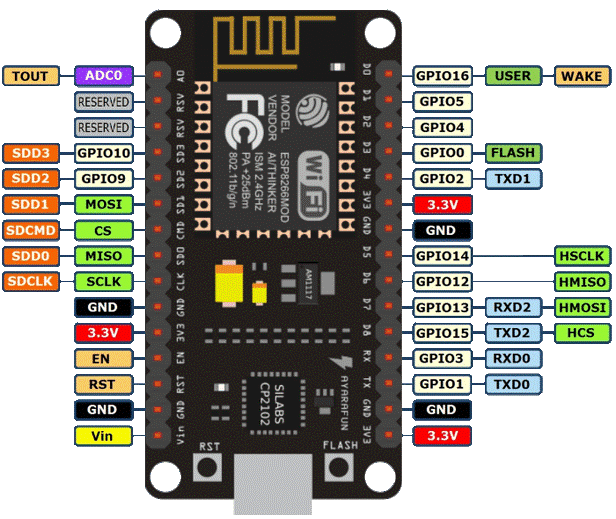
Pin Configuration
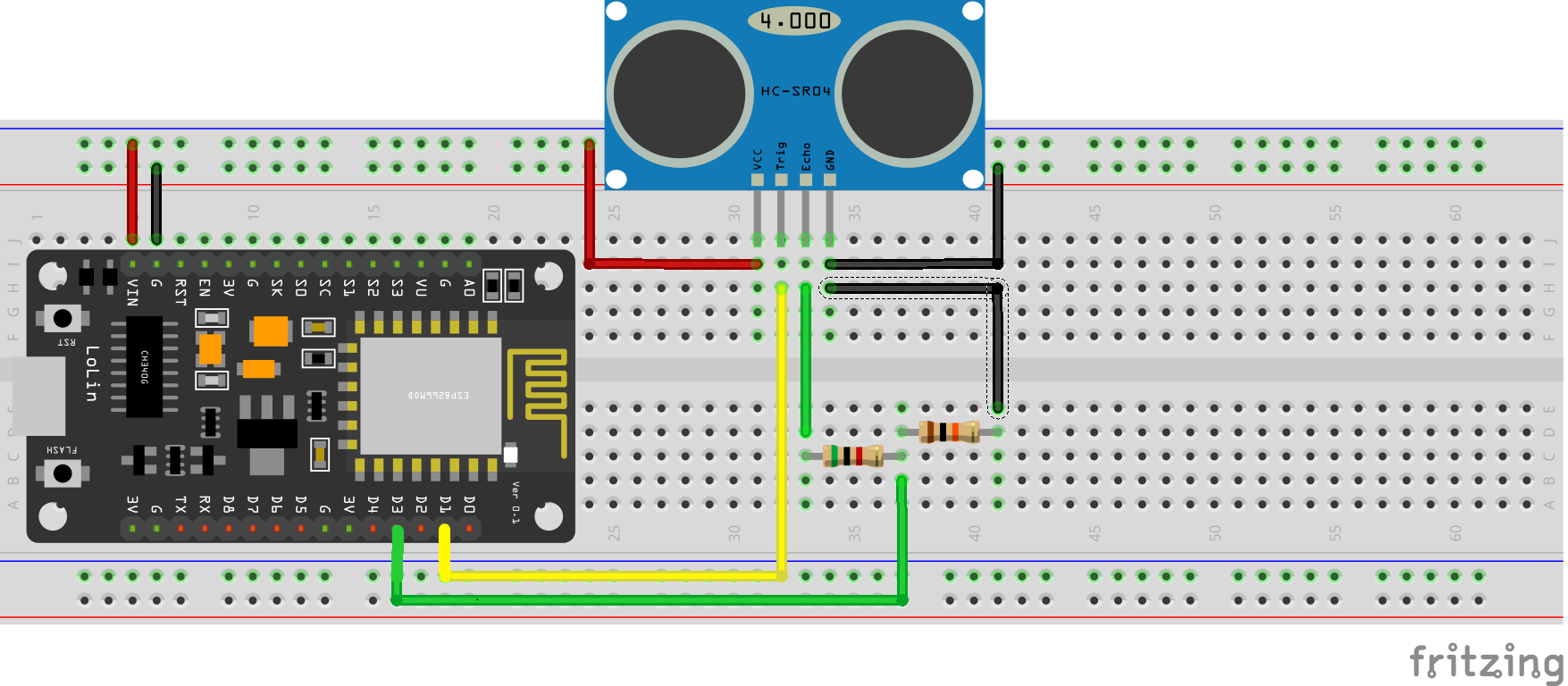
const int trigPin = D1;
const int echoPin = D3;
long duration; int distance; // VARIABLES
void setup() {
pinMode(trigPin, OUTPUT); // TRIGPIN IS OUTPUT
pinMode(echoPin, INPUT); // ECHO PIN IS INPUT
Serial.begin(9600); // 9600 BITS TRANFERING TO PC PER SECOND
}
void loop() {
digitalWrite(trigPin, LOW); // SENDING LOW PULSE FOR 2uSECONDS TO TRIGGER
delayMicroseconds(2);
digitalWrite(trigPin, HIGH); // SENDING HIGH PULSE FOR 10uSECONDS TO TRIGGER
delayMicroseconds(10);
digitalWrite(trigPin, LOW);
duration = pulseIn(echoPin, HIGH); // TO READ THE PULSE WHICH RETURN BACK THROUGH ECHO PIN
distance= duration*0.034/2; // CALUCATING DISTANCE BASED ON SOUND VELOCITY
Serial.print("Distance: ");
Serial.println(distance);
}
